Platform overview
The ThreatSTOP Platform is a collection of cloud-based services that integrate with your network devices to proactively protect networks against security threats, such as malware, ransomware, phishing and other types of malicious traffic.
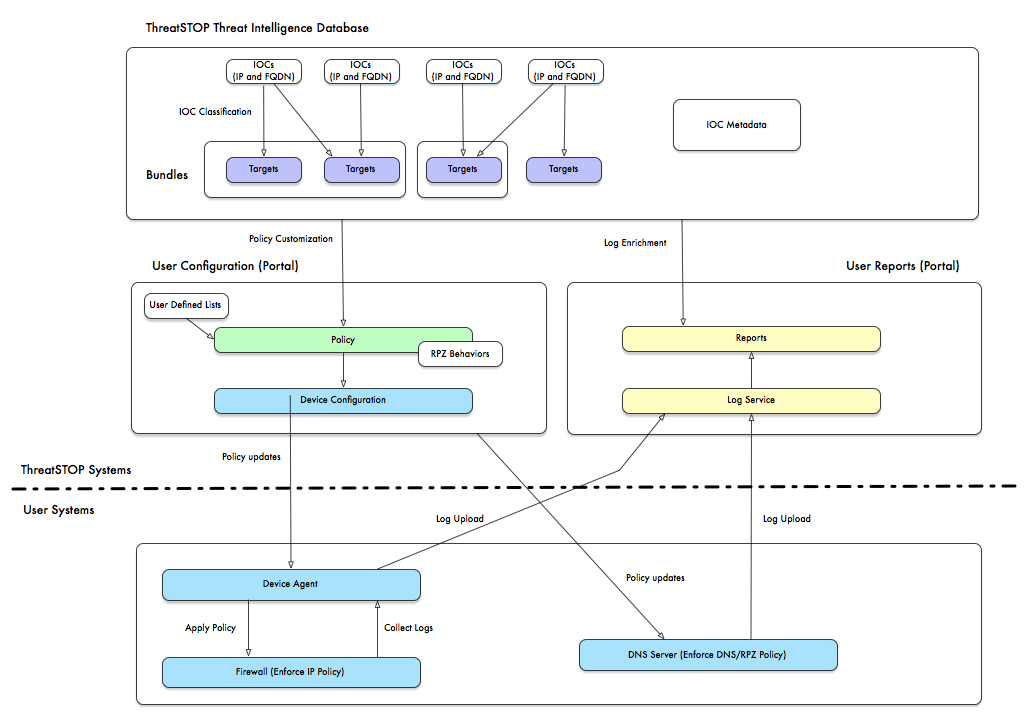
The platform produces and curates Threat Intelligence feeds into customizable policies. These policies contain up-to-date IP addresses and domains used by malicious actors. They are updated throughout the day and loaded automatically on your firewalls, routers, DNS servers and/or end-user clients.
The resulting ACLs are enforced by your existing network devices, and block:
- Outbound traffic, such as a request for an encryption key made by a machine infected by ransomware, communications with Control & Command nodes of a botnet, or a browser following a user’s click on a Phishing URL.
- Inbound traffic, such as scanners for 0-day exploits in your web or mail servers.
- DNS lookups querying for malicious domains or resolving to malicious IP addresses.
Threat Intelligence should not be limited to analyzing logs after an intrusion. By turning Threat Intelligence into enforced access lists, ThreatSTOP proactively protects your network from the intrusion.
The Threat Intelligence data is classified into targets based on multiple attributes, such as:
- The type of Threat.
- Its severity.
- The industries targeted by the Threat.
- Our confidence level in the Threat Intelligence data.
The classification allows you to customize your policy based on your organization’s security posture. It also enables reports that correlate the blocked connections and DNS lookups from your device logs with the threats.
IP and DNS traffic
The ThreatSTOP platform produces two types of policies:
- IP policies, designed for firewalls, routers and bridges. They block inbound and outbound traffic involving the malicious IP addresses. Each target can be set to block or allow traffic from/to the IP addresses currently present in it.
- DNS policies, designed for DNS servers and the ThreatSTOP MyDNS endpoint agent, which blocks malicious outbound connections by preventing your device from resolving the DNS records used to direct traffic to the malicious system. Not only can ThreatSTOP block the records based on its DNS FQDN, ThreatSTOP can also block the resolved IPs or any lookup involving a malicious DNS server, thus preventing lookups of the newest DNS names used by threat actors. Each target can be set to block or allow the DNS lookup, or even to redirect its response (typically to a Walled Garden).
How does ThreatSTOP work?
Components
There are two components required to make the ThreatSTOP platform functional: the ThreatSTOP cloud services and integration with a compatible device in your network.
- The ThreatSTOP cloud-based service, managed through a web portal. Using the portal, you will be able to:
- Create and edit your policies, choosing from pre-defined policies curated by the ThreatSTOP security team on your behalf, and custom policies that can include your own blocklist and whitelists.
- Control the assignment of policies loaded on each of your ThreatSTOP-integrated network devices.
- View and customize reports on the traffic that your policy has intercepted.
- Device integrations, which will keep your device updated with your policy using the latest Threat Intelligence.
- ThreatSTOP policies can be loaded on many Firewalls, Routers, DNS servers, as well as Windows and OSX laptops/workstations using MyDNS.
- No development or custom integration is required by your IT department. ThreatSTOP provides stand-alone software that will refresh the ACLs on your device using native and existing features.
- The list of supported devices is available here. If your device is not currently supported natively by our integrataions, you can run ThreatSTOP using one of two supported transparent bridge (Linux/IPTables, Vyos or Ubiquiti devices). You can also reach us to inquire about support your device.
- The device integrations can optionally upload logs of the blocked connections and DNS lookups to generate reports.
Concepts
- IOCS: Malicious IP addresses and domain names (“Indicators of Compromise”, or IOCs) are collected by the ThreatSTOP security team from authoritative sources.
- Targets: The ThreatSTOP security teams classifies IOCs into collections named Targets, the building blocks of a policy. While a target is typically a blacklist of malicious IOCS associated with a threat, some targets are designed as whitelists to allow traffic of networks you trust.
- Target Bundles: Dynamic groups of targets, allowing building policies based on the target attributes (e.g. all Ransomware targets)
- User-Defined Lists: UDLs are customized list of IP addresses or domains that can be added to your policy - either to block or to whitelist traffic.
- Policies: The list of IOCs generated from the Targets and User-Defined Lists you selected.
- Device entries: The description of your device(s): their manufacturer and model, assigned policy and configuration settings.
- Device integration: The software provided by ThreatSTOP to load the policy on your device. Integrations are either a low-footprint agent added to the device itself or a Linux-based virtual machine that can load the policies on all your devices.
- Reports: The ThreatSTOP cloud service can deliver reports based on the blocked connection logs. Reports can be accessed via the ThreatSTOP Admin portal. They can also be scheduled and delivered by email. Logs can also be used to generate email alerts when thresholds are reached for certain criteria (such as a critical machine that originated a high-severity ransomware connection).