Overview
This document describes how to integrate ThreatSTOP’s IP Defense with a Netgate pfSense device:
- Configuration of ThreatSTOP integration on device
- Automated retrieval and updates of IP Defense policies
- Automated collection and upload of log files
Compatibility
| Manufacturer | Version | Supported |
|---|---|---|
| Netgate | 2.5.x | Yes † |
| Netgate | 2.6.x | Yes † |
| Netgate | 2.7.0 | Yes |
| Netgate | 2.7.1 | Yes |
| Netgate | 2.7.2 | Yes |
| Netgate | 2.8.0 | Yes |
| Netgate | 2.8.1 | Yes |
- † - Netgate has deprecated some of the package repositories used by previous versions of pfSense. This package requires packages (sudo, stunnel) to function properly.
Upgrades
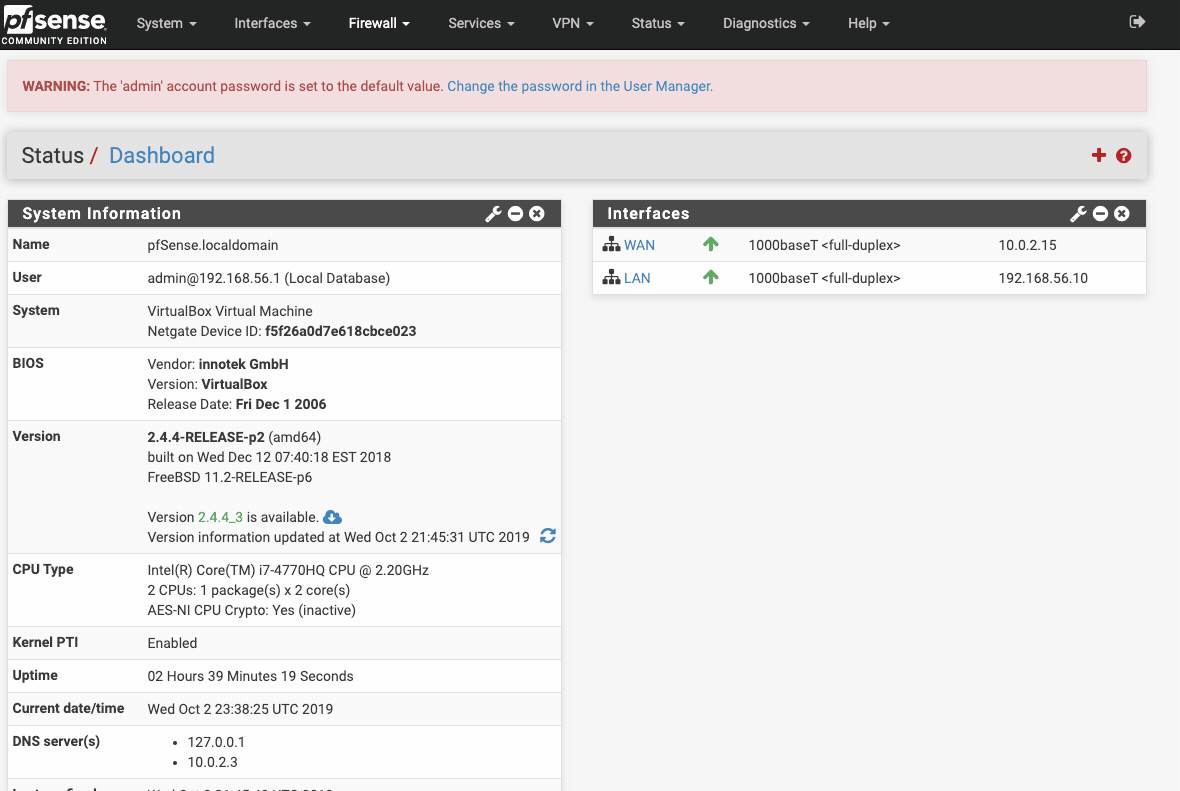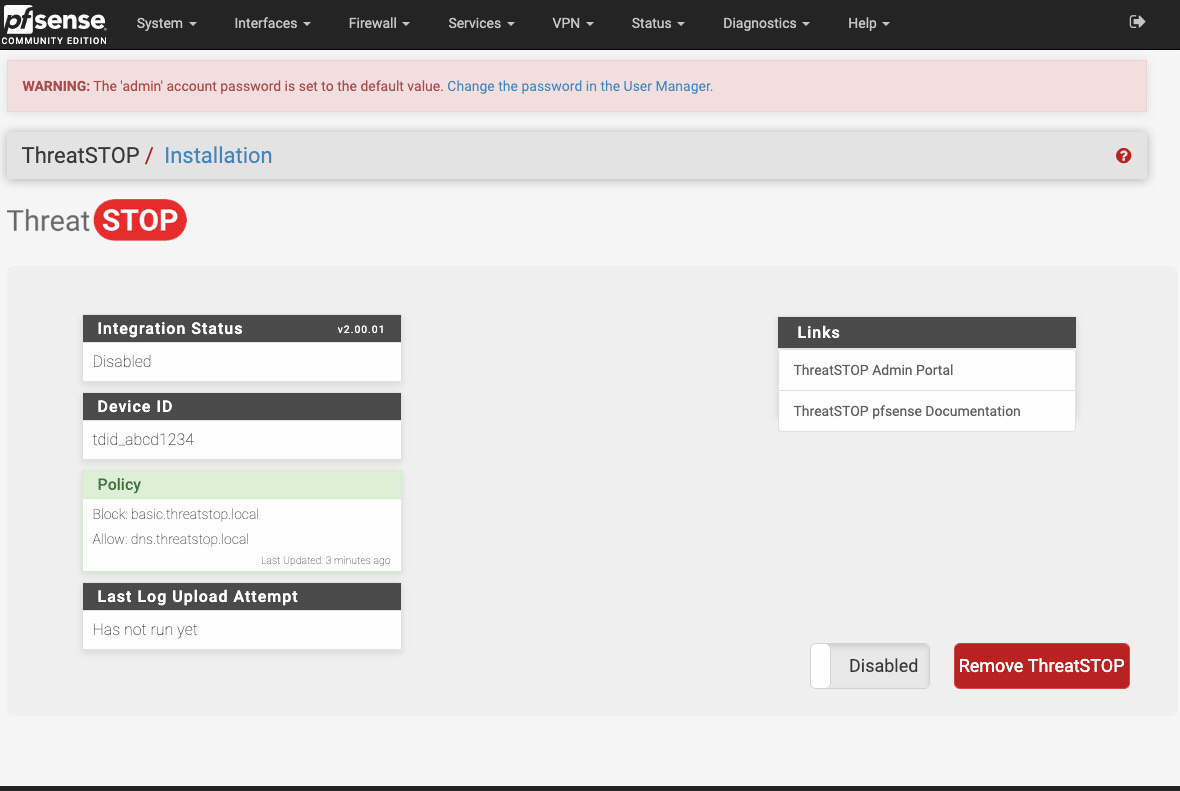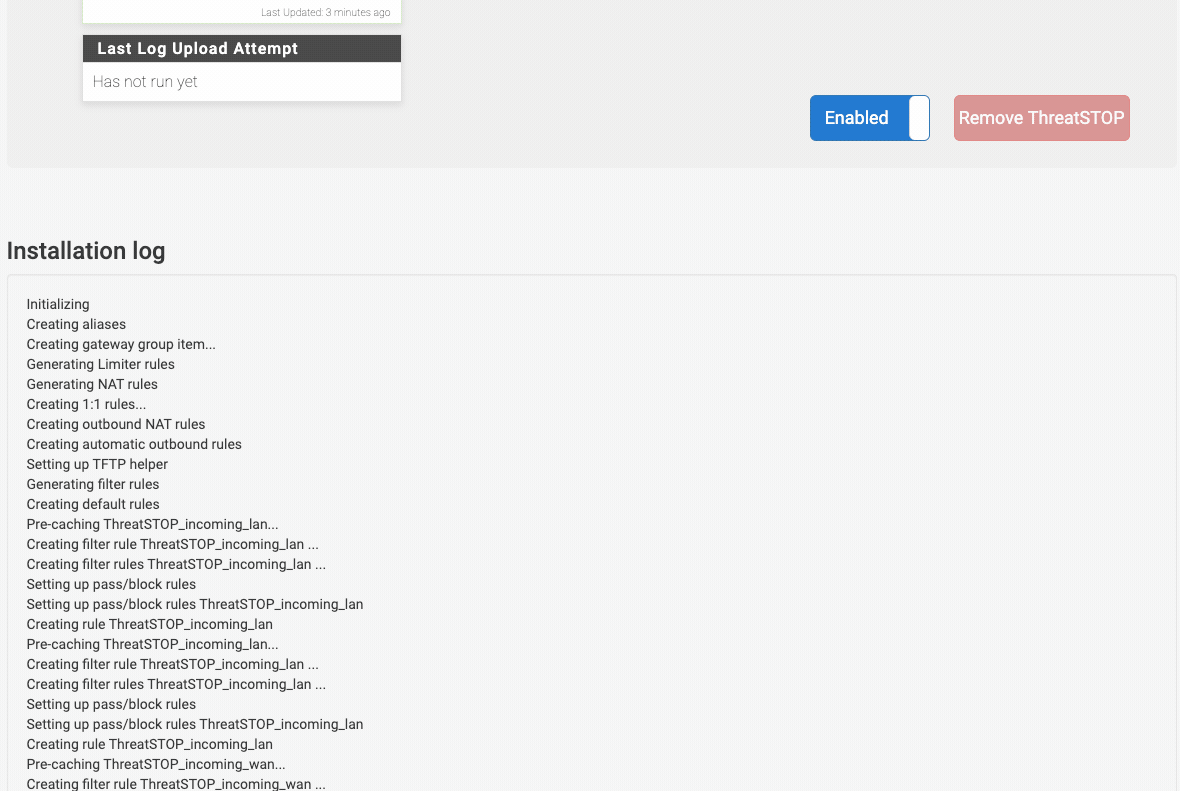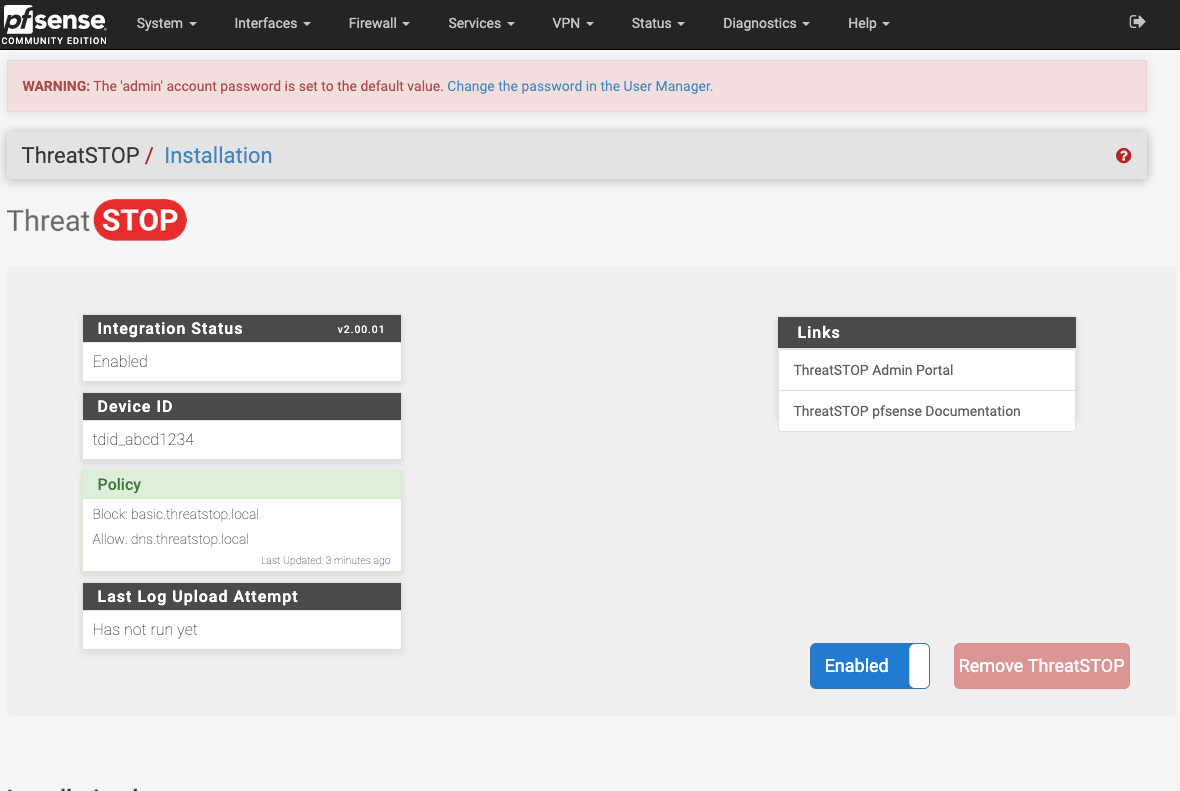
- log into the web interface and go to Firewalls > ThreatSTOP
- from this status page you’ll be able to disable, then remove the integration
- next remove the package by running
pkg remove ts-pfsense. Netgate recommends removing all packages you’ve installed prior to upgrading. - you can now proceed installing the new pfSense version.
Current Version
| Current Version | Released |
|---|---|
| 2.07-01 | Aug 20th, 2025 |
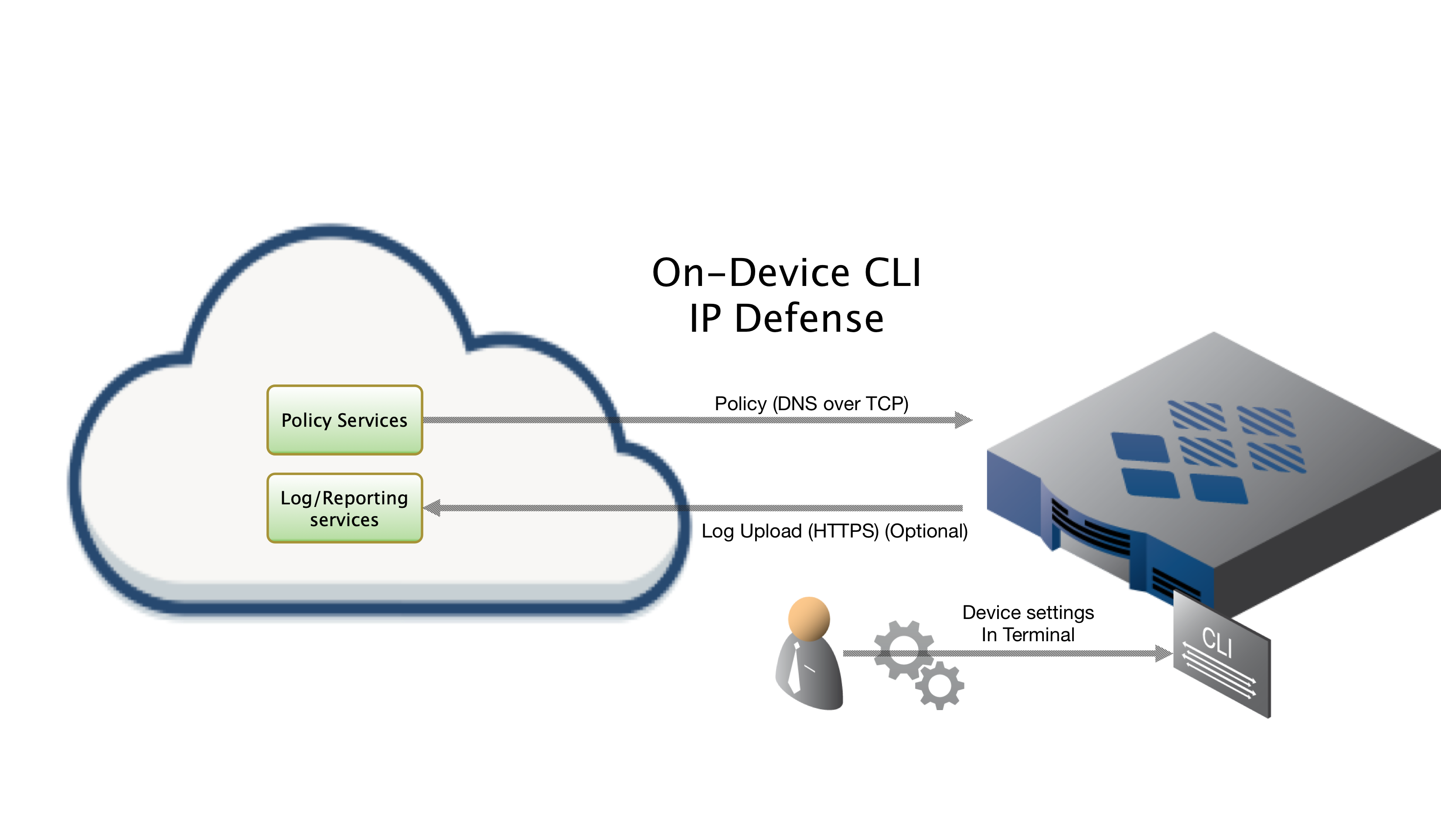
ThreatSTOP Data Flow Diagram
Install Methods
On Device CLI Install
Installing On-Device via SSH CLI setup wizard and local web interface, which is covered by this document.
On Device Install via Web Automation
Installing directly on your device via Web Automation, which allows you to configure settings on our web interface and have them automatically update on the device after initial installation. This method will require you to run an initial abbreviated command on the device to link up to our services. From that point forward your device will stay in sync with configuration updates you make on the portal. For more information regarding Web Automation here.
Quick settings
Quick settings are provided below for expert installers who have already read through the documentation and understand what they are doing.
curl -o ./ts-pfsense-2.07-01.pkg -sO https://downloads.threatstop.com/pub/ts-pfsense.pkg && pkg install ./ts-pfsense-2.07-01.pkg && rehash
# Due to recent changes in the default sudoers file you may need to switch to the threatstop service account to perform the following commands.
su - threatstop
# to verify you are now the threatstop user run id
$ id
uid=1501(threatstop) gid=1501(threatstop) groups=1501(threatstop)
# now run the tsadmin add --type auto command directly below
$ tsadmin add --block_list=[Block List] --allow_list=[Allow List] --device_id=[Device ID]
Installation considerations
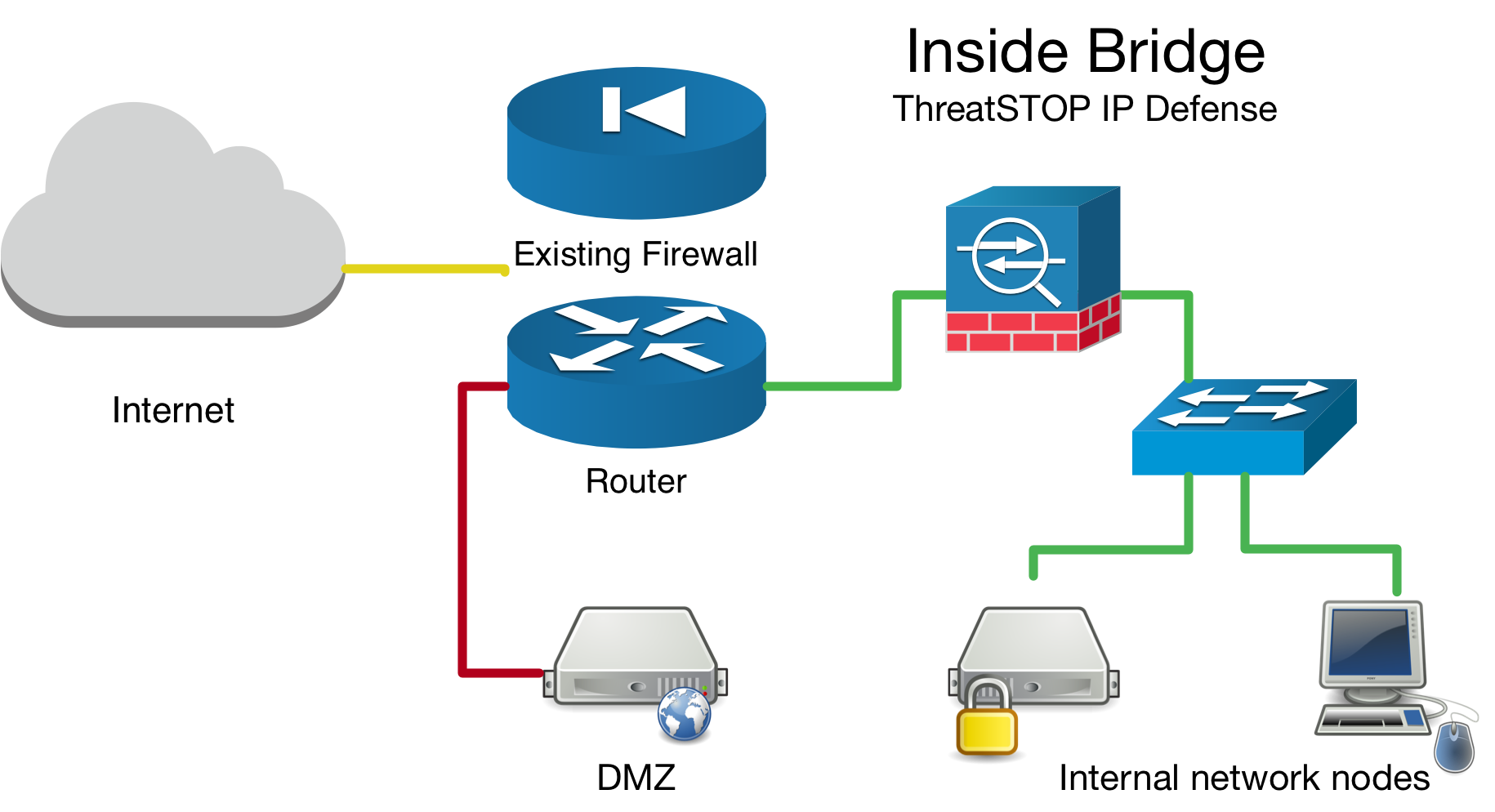
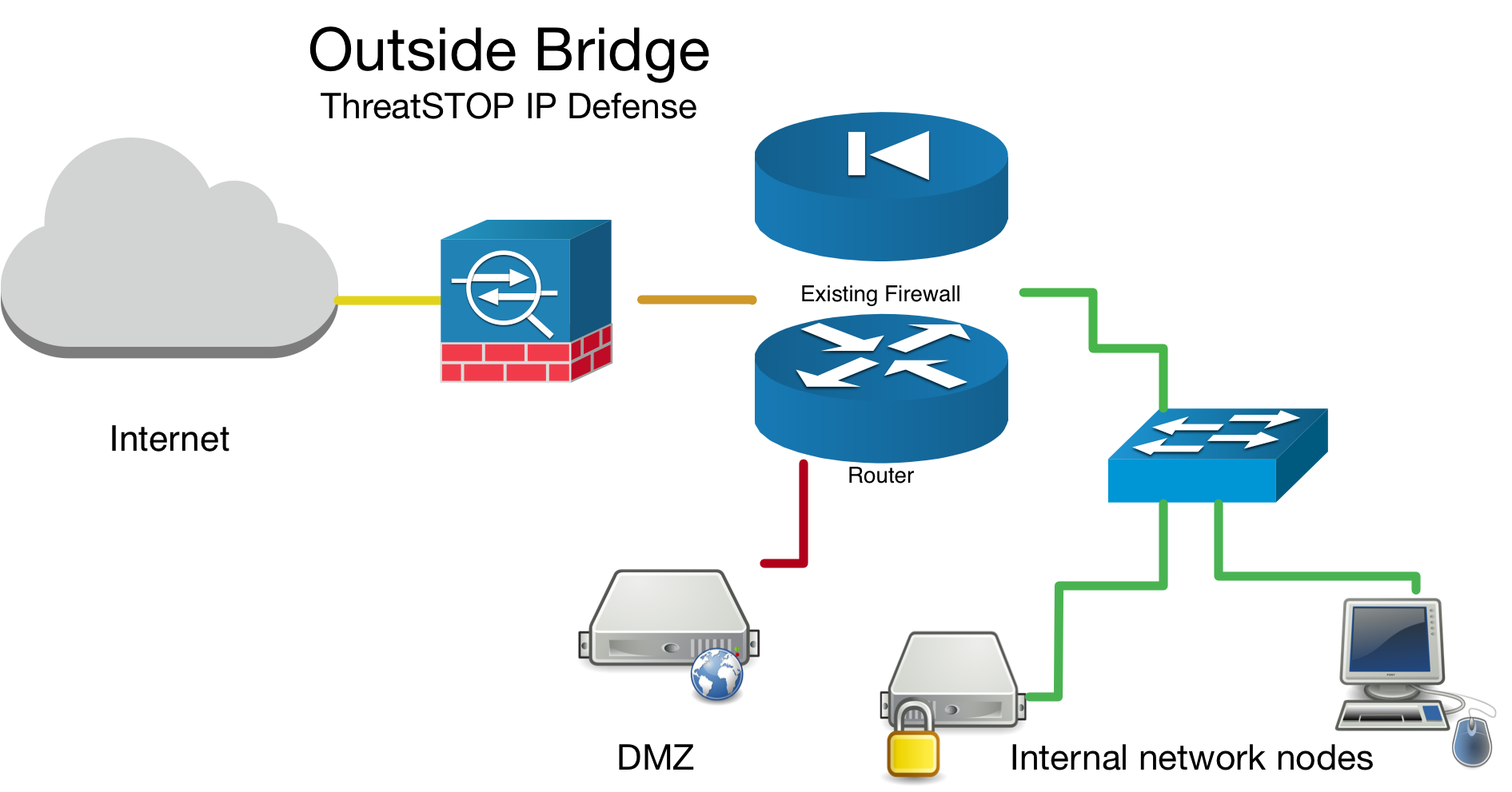
Network Bridge Considerations
If you have setup your device as a network bridge it is important to make sure you enable the Packet filter on bridge interface checkbox see this guide. Aside from bridge specific setup, the ThreatSTOP integration steps are the same for bridges as they are for routers.
More information about Netgate setting up a transparent bridge available here.
Inside Bridge Example
Outside Bridge Example
Placement of device in network topology
If you are installing this device in an environment that already has a firewall/router it is preferable to install the ThreatSTOP device “inside” the firewall/router if it is doing NAT to track down infected machines on your network. Otherwise the logs will only see the single IP address from the next hop instead of the true source node’s IP address.
Installation Parameters
If you have already created a device entry in the portal, and are familiar with the installation procedure, you can use the parameters below if you access this document from the Portal Device page and click on docs.
| Setting | Value |
|---|---|
| Device ID | Retrieved from the device settings page |
| Policy (Block List) | Retrieved from the device settings page |
| Policy (Allow List) | Retrieved from the device settings page |
Setup Command
$tsadmin add --block_list=[Block List] --allow_list=[Allow List] --device_id=[Device ID]
Installation Overview
This document will go over installation and integration of ThreatSTOP via CLI directly on your pfSense device. The basic steps are as follows:
- Add & Configure device in Admin Portal
- Install ThreatSTOP software
- Configure ThreatSTOP service on device
- Test configuration / logging.
Prerequisites
- Device added & configured via the admin portal
- Firewall Device setup as either a router or a network bridge
- SSH access to the device
- Current active ThreatSTOP account
-
Firewall table size
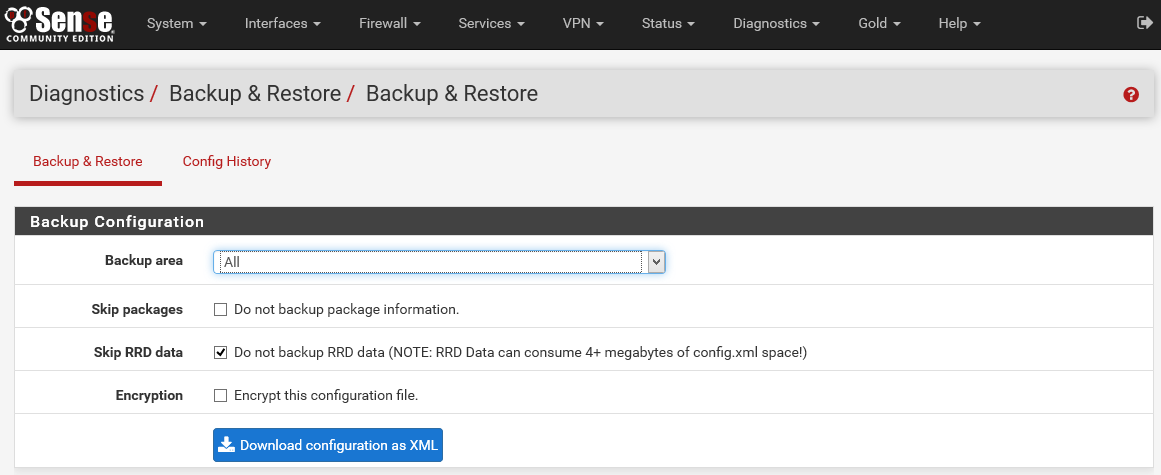
Warning: Prior to installing the ThreatSTOP package, you will need to increase the Firewall Maximum Table Entries size to at least 400,000 entries in System > Advanced, Firewall & NAT. - It is recommended that you save the current configuration before applying ThreatSTOP. This can be done from the Diagnostics: Backup/Restore page of the webConfigurator
- If you are running pfSense on a flash filesystem (or another filesystem that is read only by default) then you should temporarily mount the root filesystem as read/write. This is done by entering the following command in the SSH session:
mount -uw /
Connectivity
To retrieve its configuration and policy, and to upload log data, the firewall needs the following connectivity:
- DNS over TCP
- Hostname: ts-dns.threatstop.com
- IP Address Range: 192.124.129.0/24
- Outbound TCP port 53 or 5353
- HTTPS
- Hostname: logs.threatstop.com
- IP Address Range: 204.68.99.208/28
- Outbound TCP port 443
Setup
Step 1 - Portal device configuration
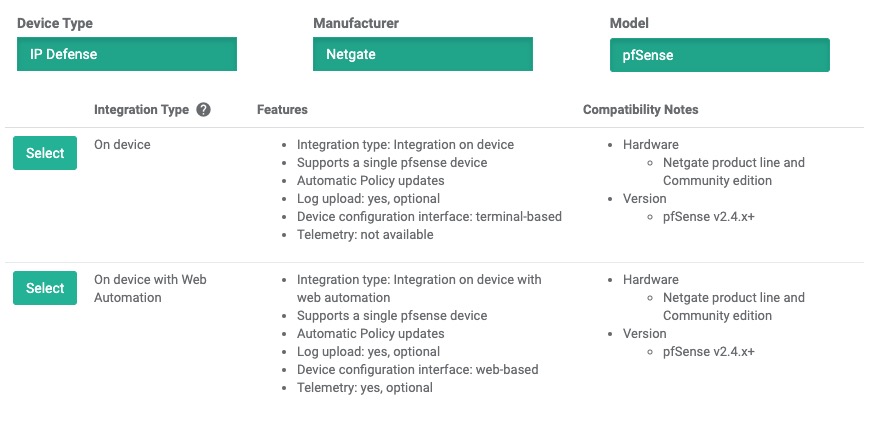
During this step, you will create a device entry on the Admin Portal. You will select a device type (Netgate > pfSense) and enter the configuration settings.
To create a pfSense device entry:
- Log into the Admin Portal with your ThreatSTOP account
- Browse to the Device page and click Add Device
- Select the device manufacturer and model:
- Type: IP Defense
- Manufacturer: Netgate
- Model: pfSense
- Integration type: On device
-
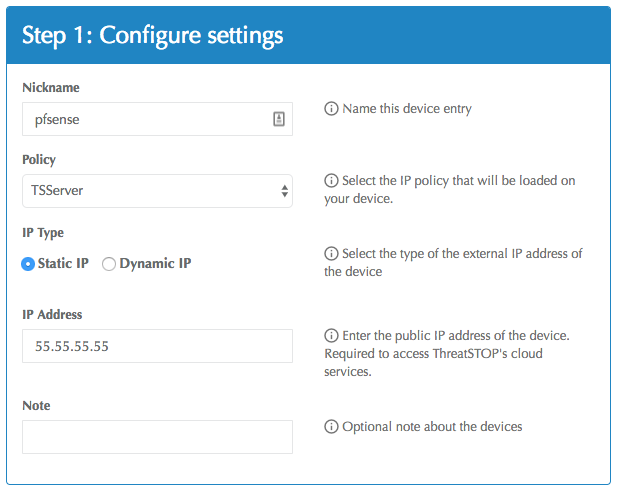
Nickname: this is a mnemonic name used to identify the device. It can be set to any string (A-Z, 0-9, - and _). If you create multiple device entries, each entry must have a unique nickname. The Nickname will be used to identify the firewall and in the Reporting user interface.
-
Policy: select a pre-defined policy or a customized policy. It must be an IP Defense Policy.
-
IP Type: Access to the ThreatSTOP services is controlled in part using an ACL allowing the device IP address to connect. If your device has a static public IP address (the most common case), select static. If your device has a dynamic public IP address address, the ThreatSTOP services can lookup the IP address using a DNS fully-qualified name (FQDN).
-
Public IP address: In static mode, this is the public IP address of the device. It is possible to configure multiple device entries with the same public IP address.
-
Domain name: In Dynamic mode, this is a DNS FQDN which must be kept up-to-date as an A record pointing to the device’s dynamic IP address.
-
Note: An optional field to store a note of your choice about the device - location, identifiers, model…
Upon saving the form, a device entry will be created in ThreatSTOP’s cloud.
Step 2 - Download software
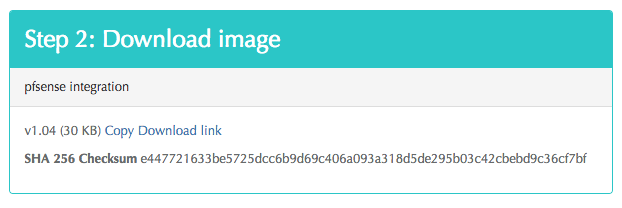
After creating the device entry, download the device software as shown below.
The download link is listed in the Step 2 section, as shown in this image.
- Click on the Copy Download Link to copy the link to your clipboard
- Using ssh, login as root to your pfSense device and type the following commands
# first we will download the software from out public repo curl -o ./ts-pfsense-2.07-01.pkg -sO https://downloads.threatstop.com/pub/ts-pfsense.pkg # For your security: after downloading the file, we encourage you to validate its SHA 256 checksum. Compute it as shown below and compare it to the checksum in the Portal. shasum -a 256 <filename> # now we install via pkg facility pkg install -y ./ts-pfsense-2.07-01.pkg && rehash # you will be prompted with some dependencies if they are not already on the system. # Due to recent changes in the default sudoers file you may need to switch to the threatstop service account to perform the following commands. su - threatstop # to verify you are now the threatstop user run id $ id uid=1501(threatstop) gid=1501(threatstop) groups=1501(threatstop) # next try running tsadmin version to see if the package is loaded into $PATH correctly $ tsadmin version ThreatSTOP ts-pfsense version starting @ Wed Oct 2 22:34:35 2019 ts-pfsense Version: 2.07-01
Step 3 - Configuration
- To install and setup the ThreatSTOP integration, Log into pfSense with the administrative account & run the following commands:
- Switch into the
threatstopservice account by runningsu - threatstop. Next run the installation command:
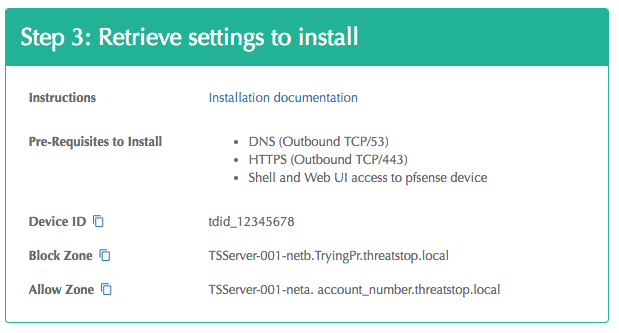
tsadmin add --block_list=[Block List] --allow_list=[Allow List] --device_id=[Device ID]
The software will install automated jobs in the crontab to perform updates and upload logs. It will also add a new page to pfSense’s webConfiguration, under the Firewall menu. Finally, it will retrieve the current version of your policy data.
The CLI installation will prompt you for the following settings if not provided via command line arguments.
-
Device ID: This is the device identification used to associate logs and settings to specific device.
-
Block list: This is the ThreatSTOP block list given in the quick settings section or referenced in the portal.
-
Allow list: This is the ThreatSTOP allow list given in the quick settings section or referenced in the portal.
-
Maximum Policy Size: Option limit on the number of entries in the policy. If the policy becomes larger than this setting, the device will truncate it down to the Maximum Policy Size.
Advanced Settings (optional)
- DNS Port: The device uses TCP Port 53 (outbound connections) to retrieve policy data. If this port is blocked or filtered (for example, networks using a DNS Application Layer Gateway), use this setting to switch to TCP Port 5353.
The final step will enable the integration using the pfSense webConfiguration.
- Open a web browser and login into the device’s webConfigurator GUI.
- If not already done, click on the System > Advanced menu then select Nat/Firewall. Set Firewall Maximum Table Entries to at least 400,000.
- Open the Firewall > ThreatSTOP menu
- Click the Enable button
-
Confirm that the installation completed ok by checking the output of the setup now displayed on the page.
- From this point on, the firewall will retrieve updates for the policy, every hour.
Step 4 - Testing Configuration
To ensure your device is properly blocking and logging traffic, test traffic to a known test address in both directions. The following logging demonstrates traffic being dropped by the firewall rule-set in both directions by the TS-inbound firewall rule set.
# first we test to see if bad.threatstop.com's IP address is being blocked. This is a safe IOC to use for testing.
admin@pfSense# dig +short bad.threatstop.com
64.87.3.133
# next, we verify it is in the ThreatSTOP block list.
admin@pfSense# grep 64.87.3.133 /var/db/aliastables/ThreatSTOP_block.txt
64.87.3.133
# The following step is best done on a client machine routing through the firewall.
# We'll try to curl or visit the address http://bad.threatstop.com to see if we can generate a block and log event.
curl bad.threatstop.com # or attempt to visit with a web browser
# check logs to confirm physical interface direction and that the ThreatSTOP rule matches in both directions
admin@pfSense# clog /var/log/filter.log | grep 64.87.3.133
Sep 20 23:37:41 pfSense filterlog: 6,,,1000000104,em1,match,block,out,4,0x0,,64,0,0,DF,6,tcp,52,64.87.3.133,192.168.56.1,80,57232,0,RA,1848334924,822794810,513,,nop;nop;TS
If you see the logged test blocks, Congratulations, you’ve now protected your network with a world class security threat feed!
Be sure to read our Portal Guide to get the most out of our advanced reporting features.
- To check the IPFW configuration, run
[2.4.3-RELEASE][admin@pfSense.localdomain]/root/ts-pfsense: pfctl -sr | grep -i threatstop pass in log quick on em0 inet from any to <ThreatSTOP_allow> flags S/SA keep state label "USER_RULE: ThreatSTOP_incoming_lan" block drop in log quick on em0 inet from any to <ThreatSTOP_block> label "USER_RULE: ThreatSTOP_incoming_lan" pass in log quick on em1 reply-to (em1 172.21.70.1) inet from <ThreatSTOP_allow> to any flags S/SA keep state label "USER_RULE: ThreatSTOP_incoming_wan" block drop in log quick on em1 reply-to (em1 172.21.70.1) inet from <ThreatSTOP_block> to any label "USER_RULE: ThreatSTOP_incoming_wan"
Logging and Reporting
If log upload is enabled, the firewall will now upload logs every 15 minutes, as long as there were connections blocked by the policy since the last upload. The logs can be analyzed in the IP Defense Reports 15 minutes after they’ve been uploaded.
Configuration changes
Changing the policy
- Update the policy assigned to the device in the Admin Portal
- Wait 15 minutes for the changes to propagate to ThreatSTOP’s policy service
- Re-run the
tsadmin removeandtsadmin addcommands with the updated block and allow policy names.
View the networks contains in the current policy
- Login into pfSense’s webConfiguration
- Open the Diagnostics > Tables menu
- Select the ThreatSTOP_block or ThreatSTOP_allow to view the subnet list.
Disable the ThreatSTOP policy
- Login into pfSense’s webConfiguration
- Open the Firewall > ThreatSTOP menu
- Click disable
Additional information
Troubleshooting
- Sorry, user root is not allowed to execute ‘/bin/sh -c /usr/local/bin/tsadmin add’ as threatstop on pfsense
This error is due to defaults in the /usr/local/etc/sudoers configuration file for the root account. You can switch into the ThreatSTOP user account threatstop by running su - threatstop or sudo su - threatstop then proceeding with the tsadmin command. Alternatively, if you wish to be able to run the commands as the standard root account you can modify the sudoers file e.g. root ALL=(root) ALL to root ALL=(root,threatstop) ALL.
- Fatal error: Uncaught TypeError: array_push(): Argument #1 ($array) must be of type array, null given in /usr/local/www/tsenable.php:213
If you have upgraded your pfSense OS e.g. 2.6.0->2.7.2, and you get the error messages above when trying to enable the policy it’s likely caused by old packages being installed via command line and not seen by the Web interface. To fix simply open up the pfSense Web UI > System > Package Manager > Search for and install sudo and stunnel packages. You should be able to enable the policy after.
-
Call to undefined function get_interface_ruleindex() There may have been a problem with a recent upgrade. You should remove all packages you’ve installed, backup your configuration, reinstall via the latest stable release media, restore the configuration, then reinstall the packages including ts-pfsense package.
- Failed to retrieve policy error message
- If you receive this error message while configuring the ThreatSTOP software, check the connectivity to the ThreatSTOP DNS service described above.
- If this is a new policy or device, wait 15 minutes for the configuration to propagate.
- If the issue persists, please contact ThreatSTOP support.
- There were error(s) loading the rules: /tmp/rules.debug:18: cannot define table bogonsv6: Cannot allocate memory - The line in question reads [18]: table persist file “/etc/bogonsv6”
- If this error is displayed after enabling ThreatSTOP in the webConfiguration, please make sure that you have increased the firewall table maximum size.
- See for additional information.
To get a list of configured settings run:
tsadmin show
To get a full list of available command line parameters on the command line type:
tsadmin --help
If you are not able to download the policy, run the following:
admin@pfSense# curl http://logs.threatstop.com/cgi-bin/validip.pl
Your IP address: 1.2.3.4
Address is in the list of authorized hosts
This will tell you if your public IP address is authorized to access the policy.
Version Changelog
| Version | Release Date | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 2.07-01 | 2025-08-20 | Support for pfSense v2.8.0, v2.8.1 |
| 2.05-05 | 2023-11-20 | Support for pfSense v2.7.2 |
| 2.05 | 2023-11-13 | Support for pfSense v2.7.0 |
| 2.04 | 2022-04-15 | Support for pfSense v2.6.0 |
| 2.03-02 | 2021-06-17 | Hostname & Telemetry bugfix |
| 2.03 | 2021-03-31 | Support for pfSense v2.5.0 |
| 2.00 | 2019-10-07 | Support for pfSense v2.4.4/ PHP7 / web automation integration / enhanced integration UX |
| 1.05 | 2018-06-07 | Support for pfSense v2.4 Error handling and UI enhancements |
Uninstalling ThreatSTOP
- To uninstall the ThreatSTOP integration:
- Login into pfSense’s webConfiguration
- Open the Firewall > ThreatSTOP menu
- Click disable
- Click Remove ThreatSTOP
- You can reinstall the software by re-running the setup procedure
- You can also remove it by running
tsadmin removewhile logged in via SSH.